-
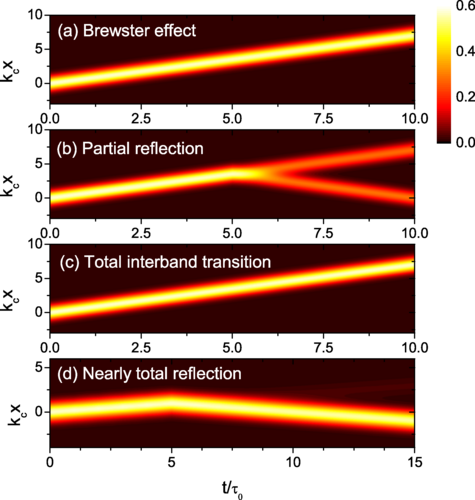
Propagation of Dirac waves through various temporal interfaces, slabs, and crystalsby Seulong Kim and Kihong KimPhys. Rev. Research 2023, 5(2), 023162; https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevResearch.5.023162AbstractWe investigate the influence of the temporal variations of various medium parameters on the propagation of Dirac-type waves in materials where the quasiparticles are described by a generalized version of the pseudospin-1/2 Dirac equation. Our considerations also include the propagation of electromagnetic waves in metamaterials with the Dirac-type dispersion. We focus on the variations of the scalar and vector potentials, mass, Fermi velocity, and tilt velocity describing the Dirac cone tilt. We derive the scattering coefficients associated with the temporal interfaces and slabs analytically and find that the temporal scattering is caused by the changes of the mass, Fermi velocity, and vector potential, but does not arise from the changes of the scalar potential and tilt velocity. We also explore the conditions under which the temporal Brewster effect and total interband transition occur and calculate the change in total wave energy. We examine bilayer Dirac temporal crystals where parameters switch between two different sets of values periodically and prove that these systems do not have momentum gaps. Finally, we assess the potential for observing these temporal scattering effects in experiments.
-
62
- 작성자박은영
- 작성일2024-02-06
- 144
- 동영상동영상
-
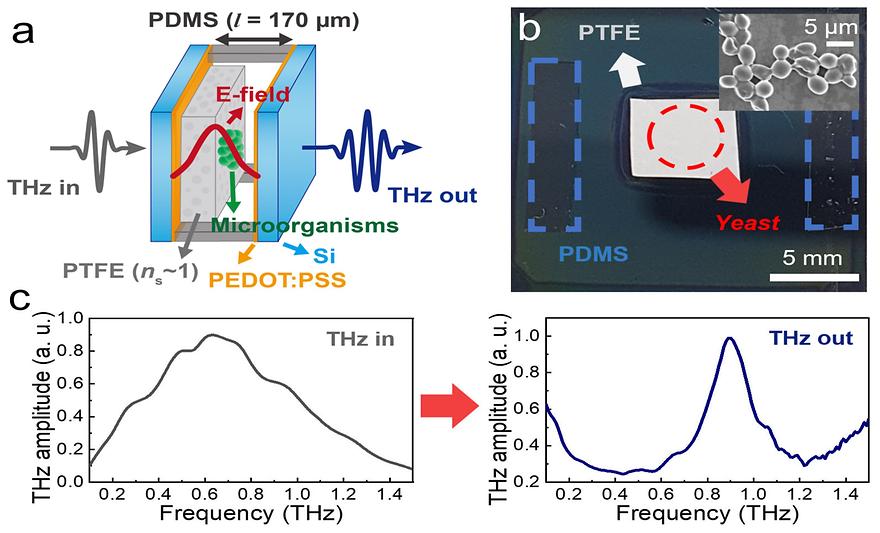
Developing a Novel Terahertz Fabry–Perot Microcavity Biosensor by Incorporating Porous Film for Yeast Sensingby Hwan Sik Kim, Seung Won Jun and Yeong Hwan AhnSensors 2023, 23(13), 5797; https://doi.org/10.3390/s23135797AbstractWe present a novel terahertz (THz) Fabry–Perot (FP) microcavity biosensor that uses a porous polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) supporting film to improve microorganism detection. The THz FP microcavity confines and enhances fields in the middle of the cavity, where the target microbial film is placed with the aid of a PTFE film having a dielectric constant close to unity in the THz range. The resonant frequency shift increased linearly with increasing amount of yeasts, without showing saturation behavior under our experimental conditions. These results agree well with finite-difference time-domain (FDTD) simulations. The sensor’s sensitivity was 11.7 GHz/μm, close to the optimal condition of 12.5 GHz/μm, when yeast was placed at the cavity’s center, but no frequency shift was observed when the yeast was coated on the mirror side. We derived an explicit relation for the frequency shift as a function of the index, amount, and location of the substances that is consistent with the electric field distribution across the cavity. We also produced THz transmission images of yeast-coated PTFE, mapping the frequency shift of the FP resonance and revealing the spatial distribution of yeast.Keywords: Fabry–Perot cavity; microorganisms; porous film
-
60
- 작성자박은영
- 작성일2024-02-06
- 137
- 동영상동영상
-
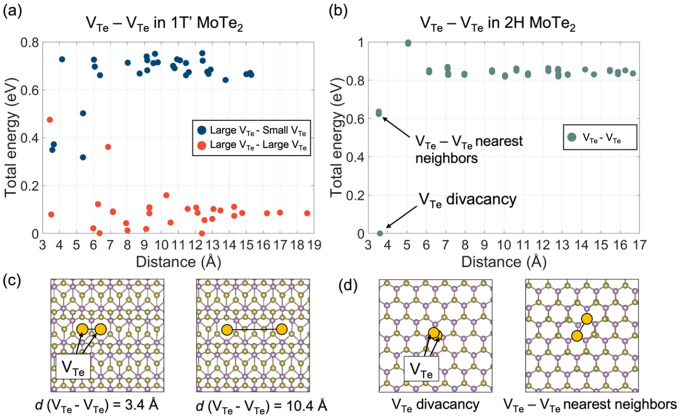
Elucidating atomistic mechanisms of the formation of phase-controlled ultrathin MoTe2 films and lateral hetero-phase MoTe2 interfacesby Hyeonkyeong Kim, Jooyong Bhang, Taejoon Park, Jae-Hyun Lee, Hosung Seo, Youngdong YooSurfaces and Interfaces 2023, 40, 103040; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2023.103040AbstractMolybdenum ditelluride (MoTe2) is gaining great attention because of its phase tunability. However, the precise control of the phase of ultrathin MoTe2 films is quite challenging, and the atomistic mechanism has not been fully elucidated. Here, we establish phase-controlled growth of ultrathin MoTe2 films by independently adjusting the Te atomic flux. We employed a chemical vapor deposition method that uses Mo nanolayers as a precursor to synthesize ultrathin MoTe2 films with a thickness of 4 − 7 nm. We found that ultrathin 1T’ MoTe2 films were formed with low Te atomic flux, whereas ultrathin 2H MoTe2 films were obtained with high Te atomic flux. Lateral metal–semiconductor hetero-phase 1T’/2H MoTe2 ultrathin films with seamless interfaces were synthesized with medium Te atomic flux. Furthermore, we performed density functional theory calculations to elucidate the detailed mechanisms of the phase transition between 1T’ and 2H MoTe2 driven by Te vacancy as well as the property of the 1T’/2H MoTe2 interface. This work provides a full understanding of the formation of phase-controlled ultrathin MoTe2 films and lateral metal–semiconductor hetero-phase MoTe2 interfaces.Keywords: Ultrathin MoTe2 films;Hetero-phase interfaces;Phase control;Te vacancies
-
58
- 작성자박은영
- 작성일2024-02-06
- 149
- 동영상동영상
-
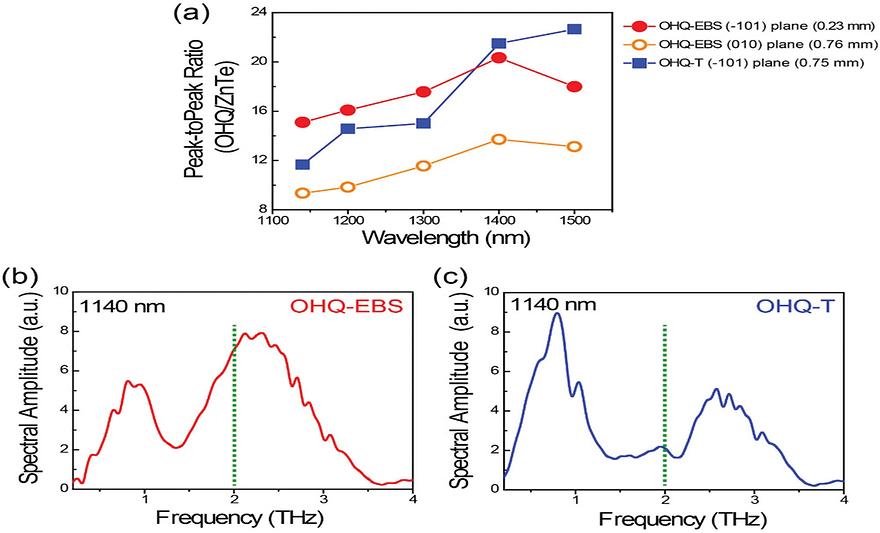
Local Rigidity by Flexibility: Unusual Design for Organic THz-Device Materialsby Dong-Joo Kim, In Cheol Yu, Mojca Jazbinsek, Chaeyoon Kim, Woojin Yoon, Hoseop Yun, Sang-Wook Kim, Dongwook Kim, Fabian Rotermund, O-Pil KwonAdvanced Optical Materials 2023, 11(21), 2300807; https://doi.org/10.1002/adom.202300807AbstractTerahertz (THz) waves interact with molecular phonon vibrations of organic matter. When designing organic THz-device materials, conformational flexible groups (CFGs) are in most cases avoided. CFGs create many low-energy conformers with high conformational entropy, which results in large and many phonon vibration modes that lead to undesired self-absorption of THz waves. Here, nonpolar CFGs only having weak intermolecular interaction capability are unusually introduced into organic THz-device materials, utilized for efficient THz wave generation. Newly designed THz-source crystals possess nonpolar methylene (CH2)n units having high conformational flexibility. Compared to previously reported benchmark crystals without methylene CFGs, introducing methylene CFGs significantly reduces void volume in newly designed crystals. This leads to the suppression of molecular phonon vibrations below 2.0 THz (i.e., introducing flexibility results in local rigidity). At infrared pump wavelengths, new CFG-contained crystals generate a strong THz electric field that is one order of magnitude stronger than that generated in inorganic ZnTe crystals. CFG-contained crystals exhibit a flatter spectral shape of the generated THz wave than benchmark crystals without methylene CFGs. Therefore, the introduction of CFGs is a very intriguing design strategy for organic THz-device materials to reduce the limitations caused by phonon vibrations.
-
56
- 작성자박은영
- 작성일2024-02-06
- 117
- 동영상동영상
-
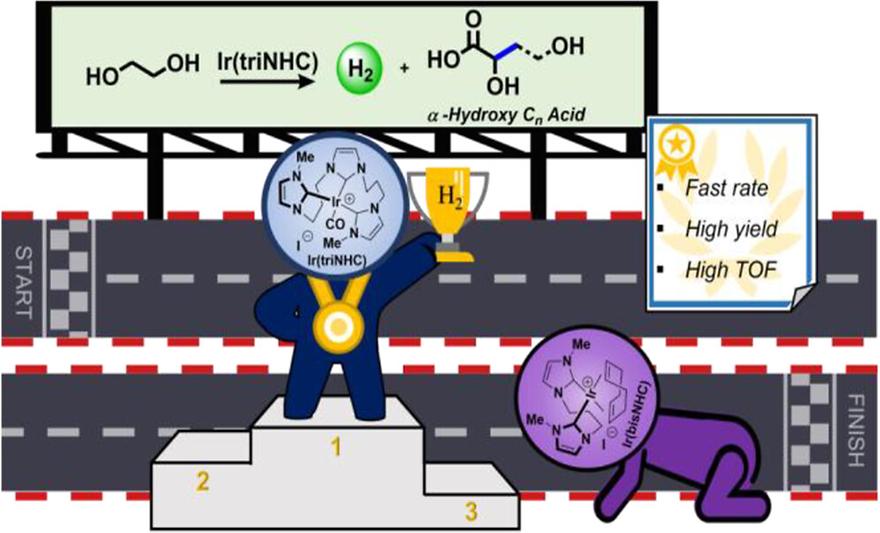
Ir(tri-N-Heterocyclic Carbene)-Catalyzed Production of Hydrogen and Cn Acids from Ethylene Glycolby Mi-hyun Lee, Heemin Byeon, Siwon Kim, Woojin Yoon, Juneseo Park, Hoseop Yun, Sungju Yu, and Hye-Young JangACS Sustainable Chem. 2023, 11(24), 8901–8907; https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.3c00950AbstractNovel tri-N-heterocyclic carbene (triNHC)-coordinated iridium catalysts (Ir(triNHC)) were employed for generating clean hydrogen and useful Cn acids from biomass-derived alcohols. The high efficiency and fast rate of hydrogen production (maximum turnover frequency = 13,080 h–1 and 485 L of H2/g-cat·h) from sustainable ethylene glycol were elucidated by the increased electron-richness of Ir(triNHC) complexes where three NHC ligands were coordinated to an iridium(I) ion. Elaborated mechanistic studies support the proposed reaction mechanisms forming H2 and Cn acids. This Ir(triNHC)-catalyzed process converting sustainable alcohols to useful fuels and chemicals is a promising carbon-neutral process.Keywords: sustainable; H2 production; α-hydroxy acid; ethylene glycol; tri-carbene
-
54
- 작성자박은영
- 작성일2024-02-06
- 122
- 동영상동영상
-
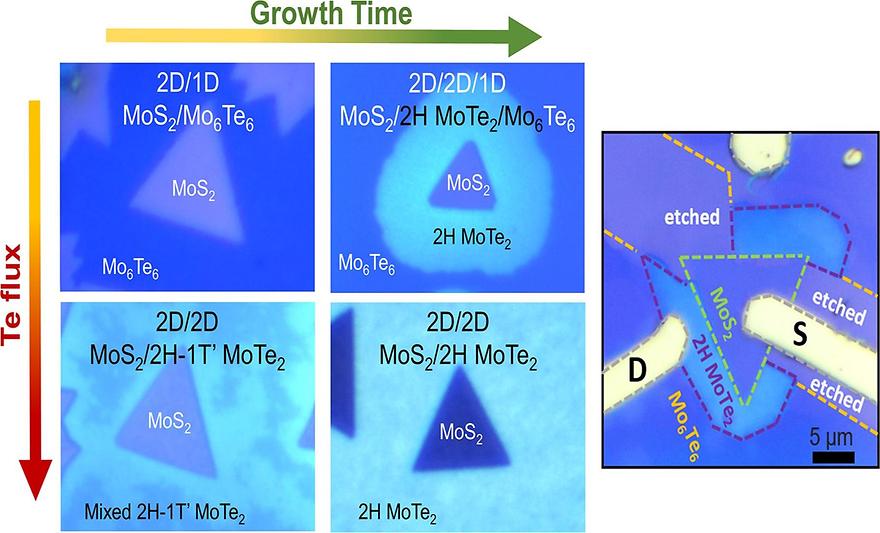
In-plane mixed-dimensional 2D/2D/1D MoS2/MoTe2/Mo6Te6 heterostructures for low contact resistance optoelectronicsby Hyeonkyeong Kim, Young Chul Kim, Yeong Hwan Ahn, Youngdong YooChemical Engineering Journal 2023, 468, 143678; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2023.143678AbstractMixed-dimensional heterostructures formed by combining 2D materials and other dimensional (0D, 1D, and 3D) materials provide new opportunities for various applications owing to their novel properties. However, in-plane mixed-dimensional heterostructures have been rarely investigated. Here, we report a novel flux-controlled chemical vapor deposition method for synthesizing in-plane mixed-dimensional heterostructures composed of monolayer MoS2 and low-dimensional Mo/Te compounds. By adjusting the Te flux and growth time, we controlled the composition, dimension, and phase of the Mo/Te compounds interfaced with the MoS2. While in-plane 2D/1D MoS2/Mo6Te6 and 2D/2D/1D MoS2/2H MoTe2/Mo6Te6 heterostructures were obtained with a low Te flux, in-plane 2D/2D MoS2/mixed 2H-1T’ MoTe2 and 2D/2D MoS2/2H MoTe2 heterostructures were synthesized with a high Te flux. We investigated the transport properties of the devices fabricated with in-plane mixed-dimensional 2D/2D/1D MoS2/2H MoTe2/Mo6Te6 heterostructures and imaged localized electronic band structures using scanning photocurrent microscopy. Under the low bias condition, the device exhibited an Ohmic-like behavior, which has not been achieved in conventional devices with stacked van der Waals junctions. Under the high bias condition, the device showed a rectifying behavior because of band-bending formed at the heterojunctions; this is consistent with the electronic band-alignment expected from the bandgap and electron affinity of the materials.Keywords: MoS2; MoTe2; Mo6Te6; Mixed-dimensional heterostructures; Edge contact
-
52
- 작성자박은영
- 작성일2024-02-06
- 125
- 동영상동영상
-
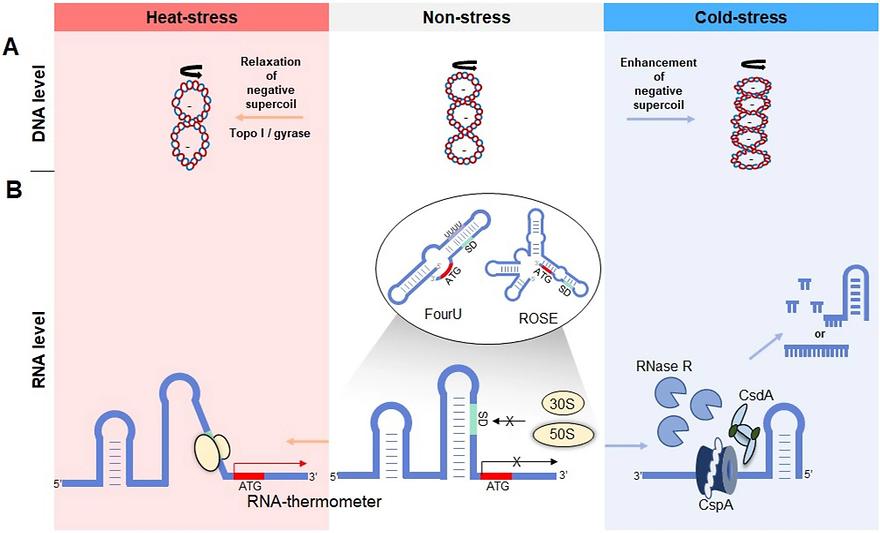
Temperature Matters: Bacterial Response to Temperature Changeby Seongjoon Moon, Soojeong Ham, Juwon Jeong, Heechan Ku, Hyunhee Kim & Changhan LeeJournal of Microbiology 2023, 61, 343–357; https://doi.org/10.1021/acsaem.3c00130AbstractTemperature is one of the most important factors in all living organisms for survival. Being a unicellular organism, bacterium requires sensitive sensing and defense mechanisms to tolerate changes in temperature. During a temperature shift, the structure and composition of various cellular molecules including nucleic acids, proteins, and membranes are affected. In addition, numerous genes are induced during heat or cold shocks to overcome the cellular stresses, which are known as heat- and cold-shock proteins. In this review, we describe the cellular phenomena that occur with temperature change and bacterial responses from a molecular perspective, mainly in Escherichia coli.Keywords: Heat shock; Cold shock; Thermosensor; Heat shock protein; Chaperone; Cold shock protein
-
50
- 작성자박은영
- 작성일2024-02-06
- 103
- 동영상동영상
-
-
48
- 작성자박은영
- 작성일2024-02-06
- 120
- 동영상동영상
-
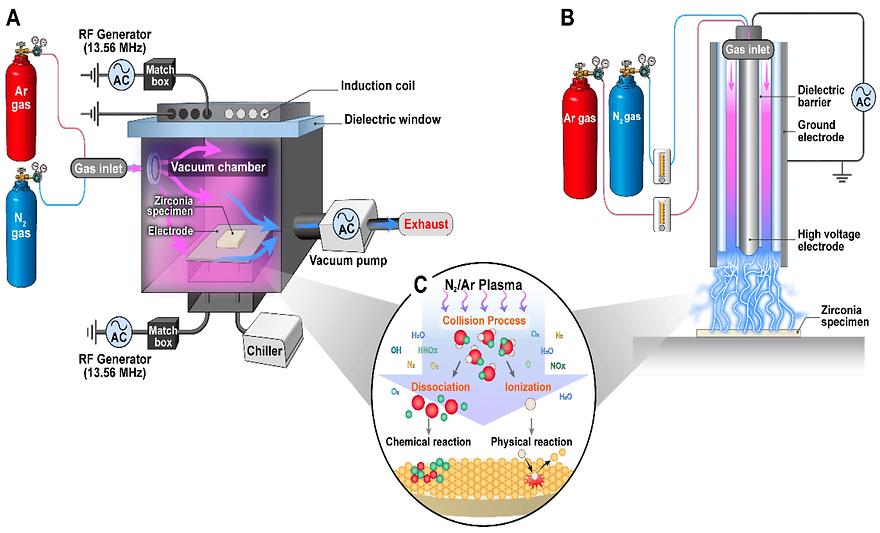
Plasma Surface Modification of 3Y-TZP at Low and Atmospheric Pressures with Different Treatment Times by Sung Un Kang, Chul-Ho Kim, Sanghyun You, Da-Young Lee, Yu-Kwon Kim , Seung-Joo Kim, Chang-Koo Kim, Hee-Kyung Kim International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2023, 24(8), 7663; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24087663 AbstractThe efficiency of plasma surface modifications depends on the operating conditions. This study investigated the effect of chamber pressure and plasma exposure time on the surface properties of 3Y-TZP with N2/Ar gas. Plate-shaped zirconia specimens were randomly divided into two categories: vacuum plasma and atmospheric plasma. Each group was subdivided into five subgroups according to the treatment time: 1, 5, 10, 15, and 20 min. Following the plasma treatments, we characterized the surface properties, including wettability, chemical composition, crystal structure, surface morphology, and zeta potential. These were analyzed through various techniques, such as contact angle measurement, XPS, XRD, SEM, FIB, CLSM, and electrokinetic measurements. The atmospheric plasma treatments increased zirconia’s electron donation (?−) capacity, while the vacuum plasma treatments decreased ?− parameter with increasing times. The highest concentration of the basic hydroxyl OH(b) groups was identified after a 5 min exposure to atmospheric plasmas. With longer exposure times, the vacuum plasmas induce electrical damage. Both plasma systems increased the zeta potential of 3Y-TZP, showing positive values in a vacuum. In the atmosphere, the zeta potential rapidly increased after 1 min. Atmospheric plasma treatments would be beneficial for the adsorption of oxygen and nitrogen from ambient air and the generation of various active species on the zirconia surface.Keywords: plasma gases; zirconium oxide; surface properties; atmospheric pressure; vacuum
-
46
- 작성자박은영
- 작성일2024-01-16
- 122
- 동영상동영상
-
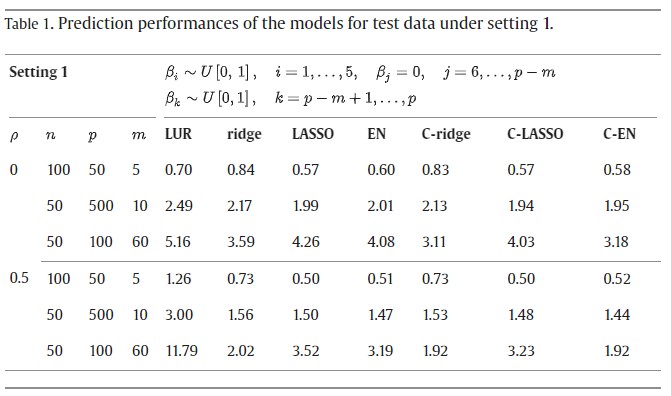
Reformulating land-use regression method as sign-constrained regularized regressions: Advantages and improvementsby Soon-Sun Kwon, Hosik Choi, Whanhee Lee, Yeonjin Kim, Hwan-Cheol Kim, Woojoo LeeEnvironmental Modelling & Software 2023, 11(12), 105653; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2023.105653AbstractLand-use regression is a popular method for predicting ambient pollutant concentrations at points of interest where no measurements are taken. However, the model-building process is complicated, and systematically understanding when and how the process works is difficult. To overcome these limitations, we reformulate the existing land use regression method as a sign-constrained regression problem with an explicit objective function to be minimized. This novel formulation always leads to estimated regression coefficients that satisfy the predefined direction based on subject matter knowledge while simultaneously substantially improving the prediction performance of the existing land-use regression method. The advantages of the proposed sign-constrained regression method are confirmed through a numerical study and real data analysis.Keywords: Land use regression; Sign constraints; Penalized regression methods; Prediction; Interpretability
-
44
- 작성자박은영
- 작성일2024-01-16
- 120
- 동영상동영상